Abstract
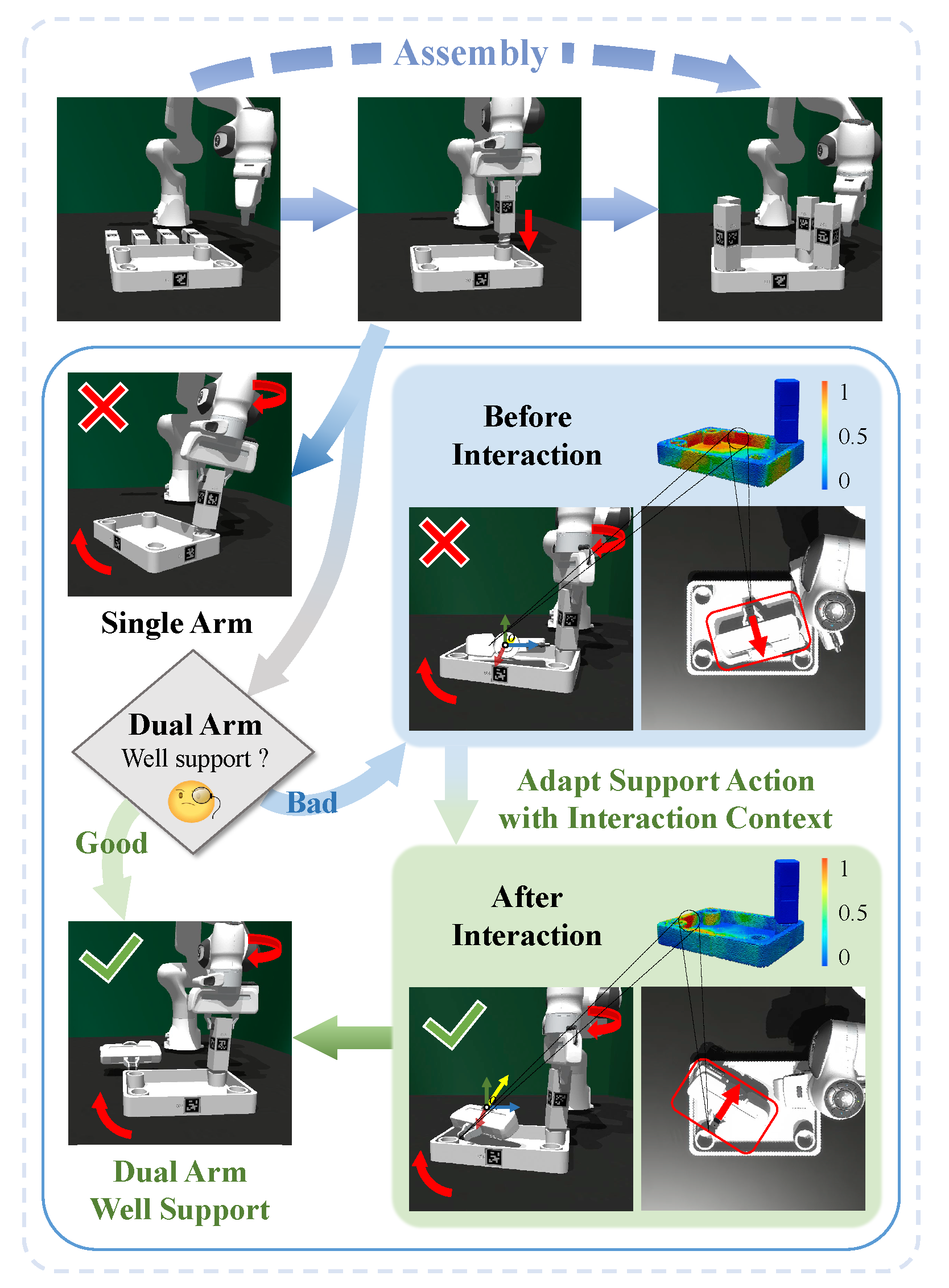
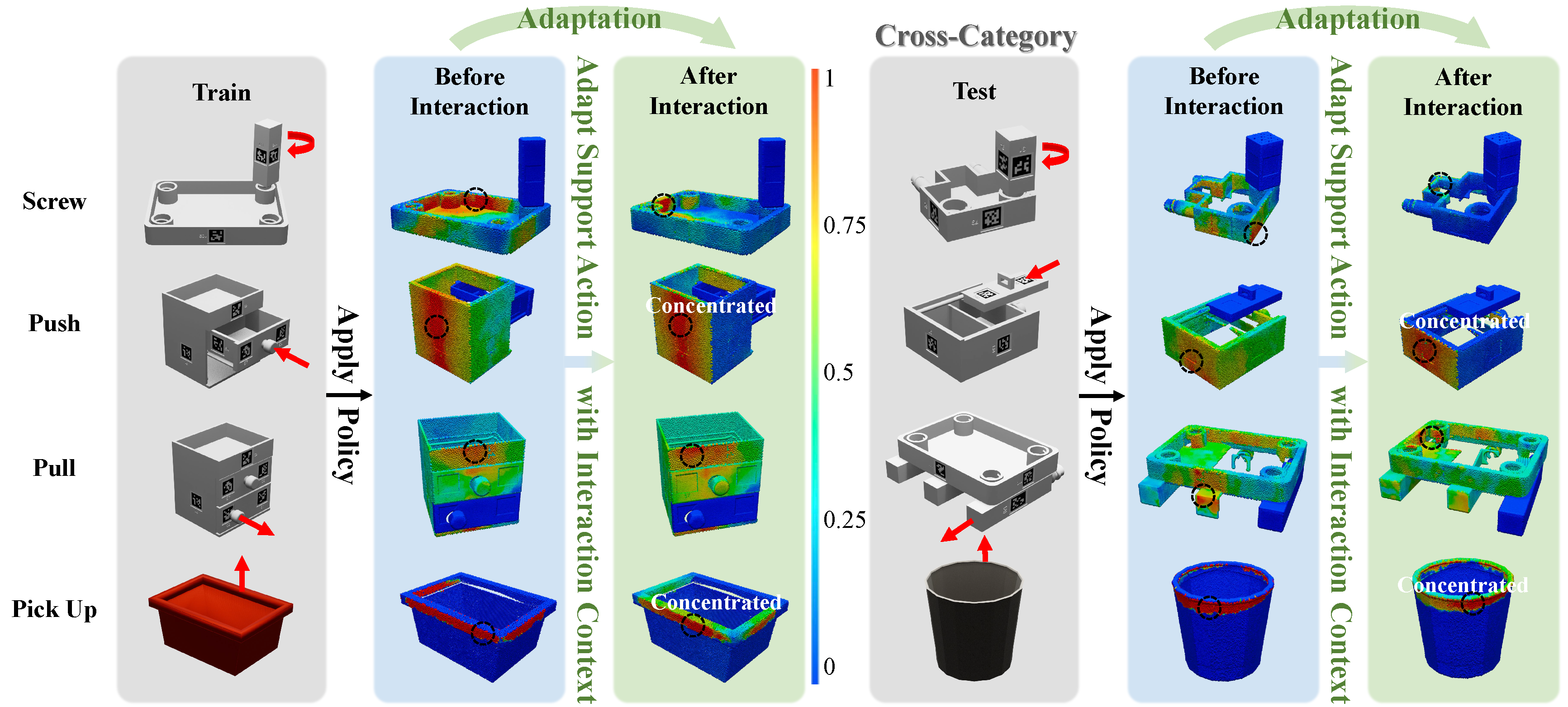
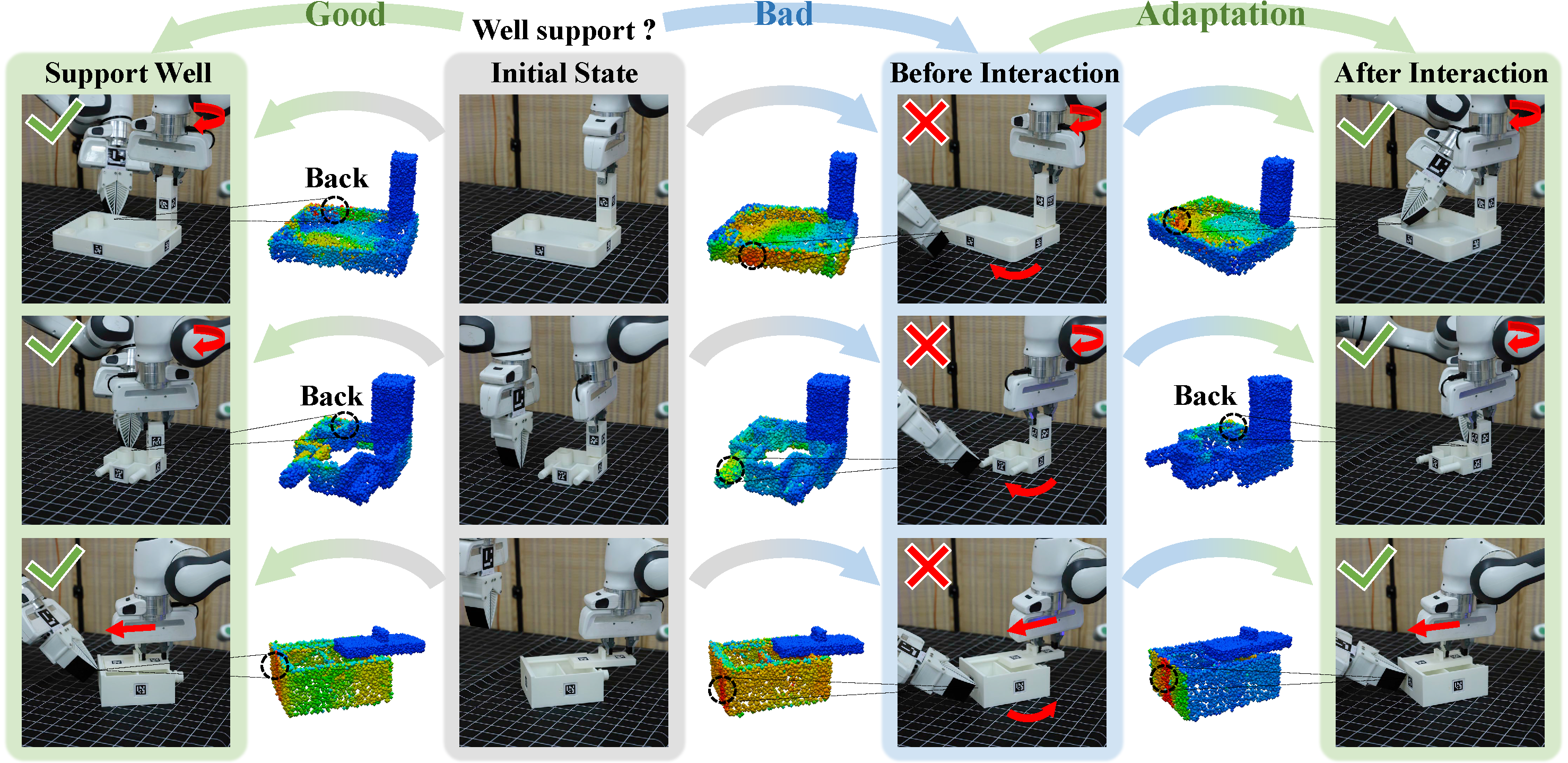
Furniture assembly is a crucial yet challenging task for robots, requiring precise dual-arm coordination where one arm manipulates parts while the other provides collaborative support and stabilization. To accomplish this task more effectively, robots need to actively adapt support strategies throughout the long-horizon assembly process, while also generalizing across diverse part geometries.
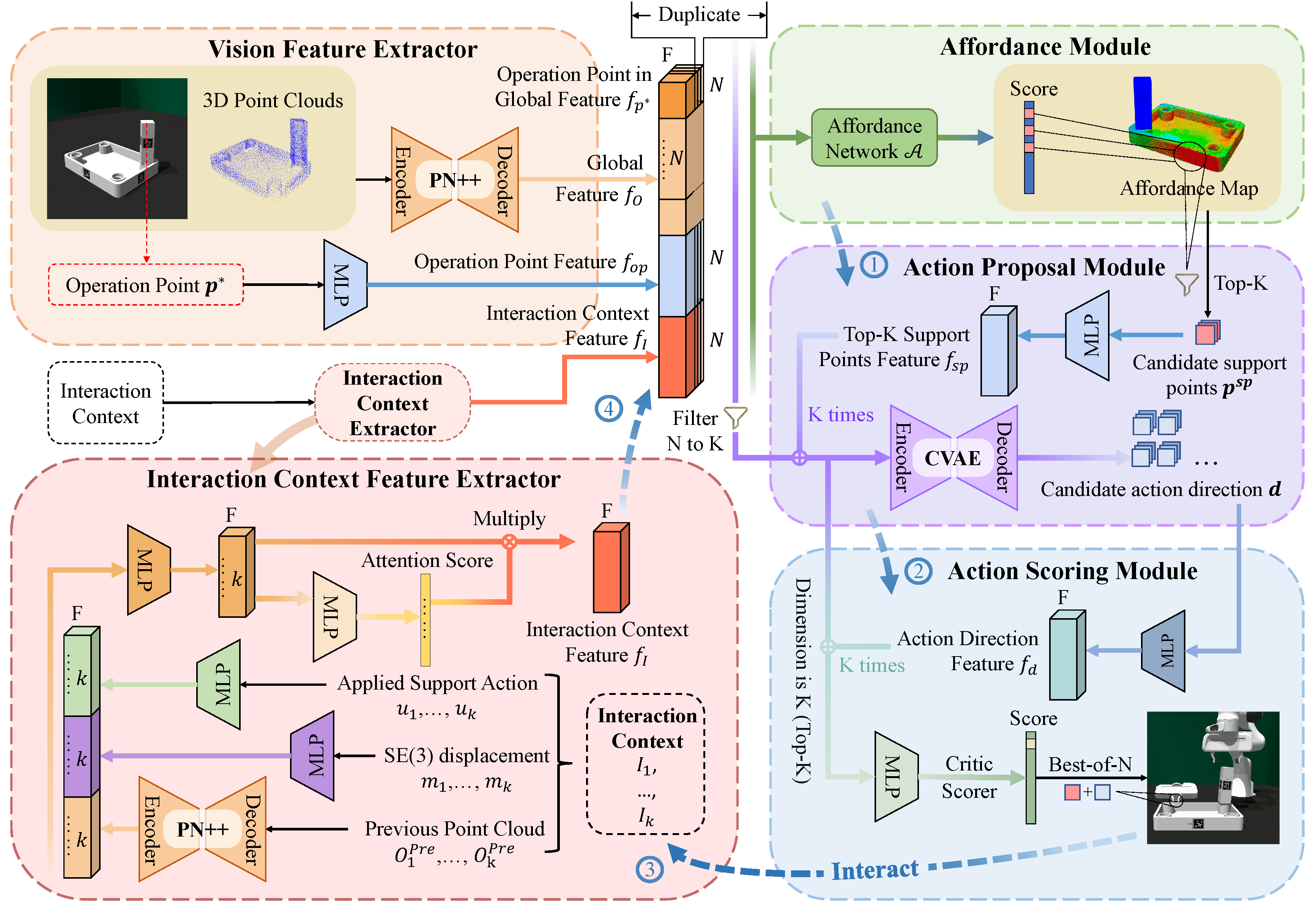
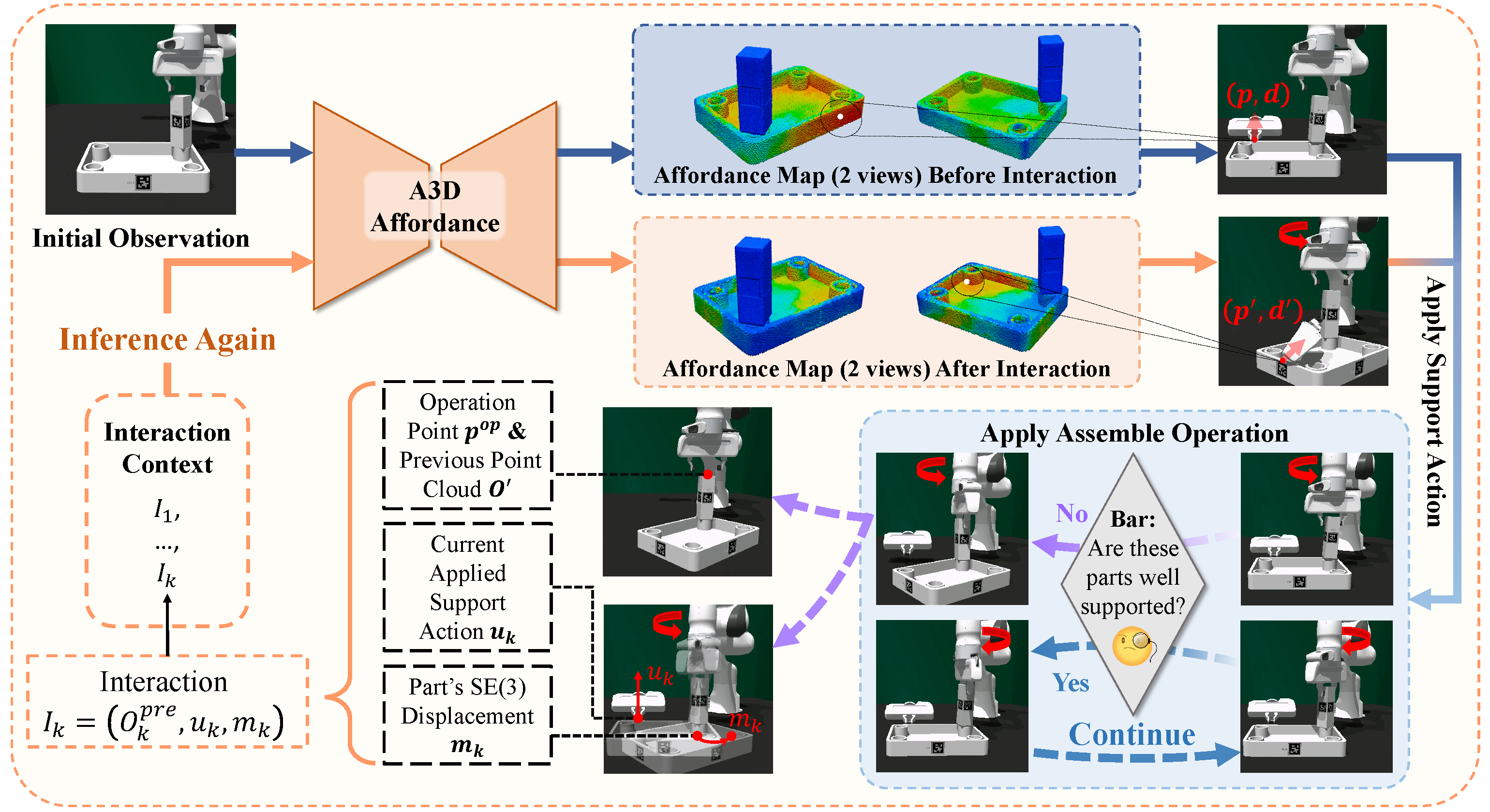
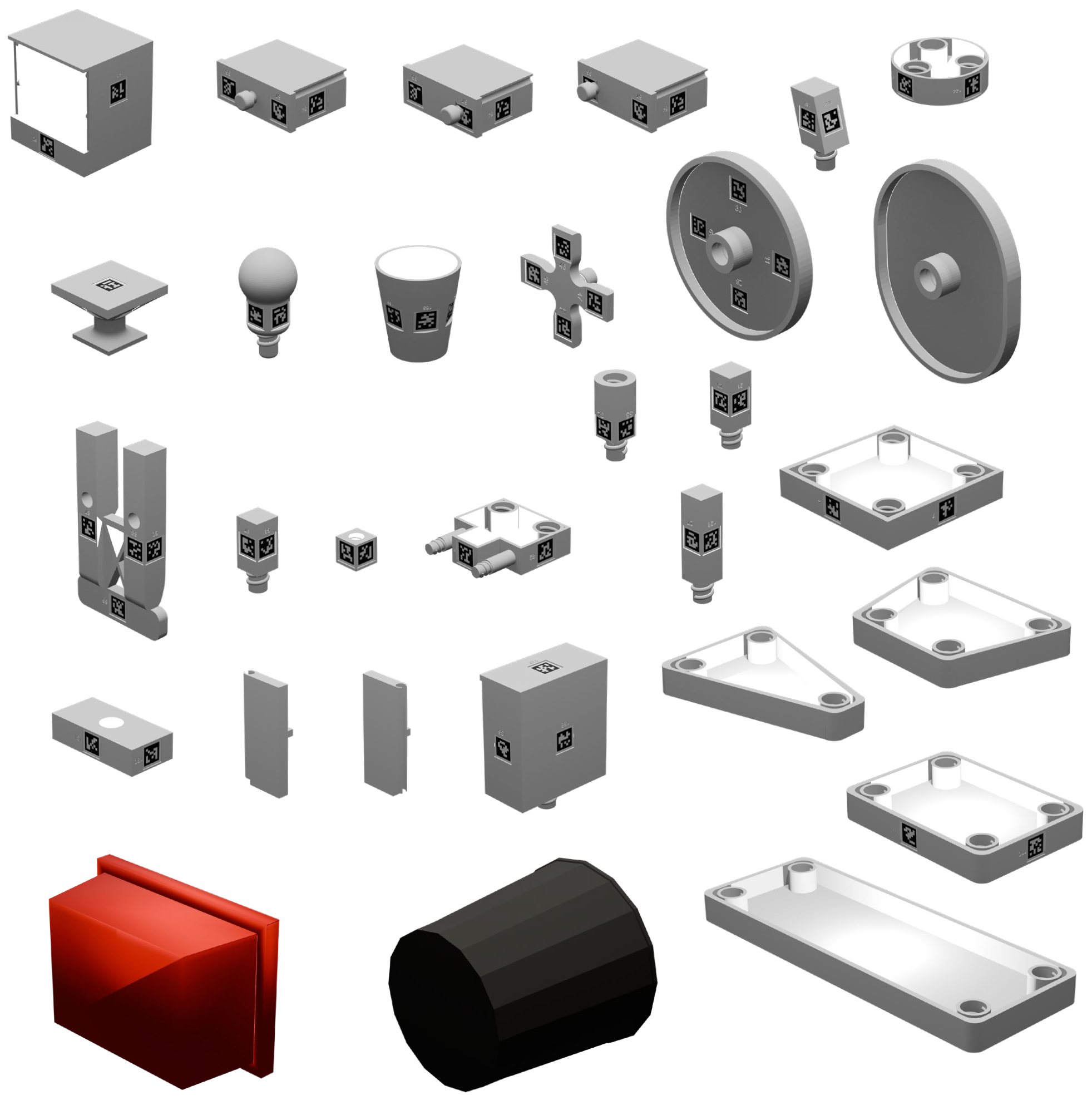
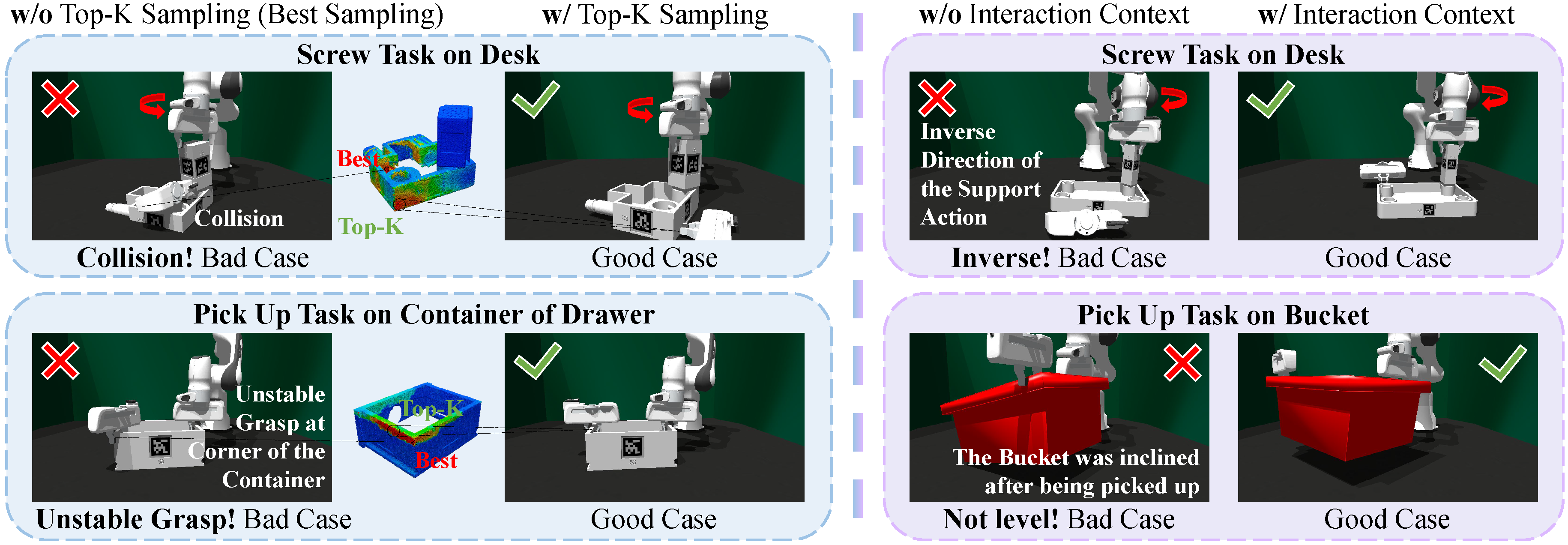
We propose A3D, a framework which learns adaptive affordances to identify optimal support and stabilization locations on furniture parts. The method employs dense point-level geometric representations to model part interaction patterns, enabling generalization across varied geometries. To handle evolving assembly states, we introduce an adaptive module that uses interaction feedback to dynamically adjust support strategies during assembly based on previous interactions. We establish a simulation environment featuring 50 diverse parts across 8 furniture types, designed for dual-arm collaboration evaluation. Experiments demonstrate that our framework generalizes effectively to diverse part geometries and furniture categories in both simulation and real-world settings.